Recently, antihyperglycemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and lipid-lowering potential of two fractions (2.5% and 5%) of P. marsupium extract (PME) was evaluated in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats.
Albino male Wistar rats were treated with a single intraperitoneal injection of STZ (45 mg/kg) to induce diabetes. Later, diabetic rats were randomly treated with the two fractions P. marsupium in a dose-dependent manner (50, 100, and 200 mg/kg) for 45 days. Blood samples were collected at the end of the study to estimate different biochemical parameters, while pancreas and liver tissues were subjected to histopathological evaluation.
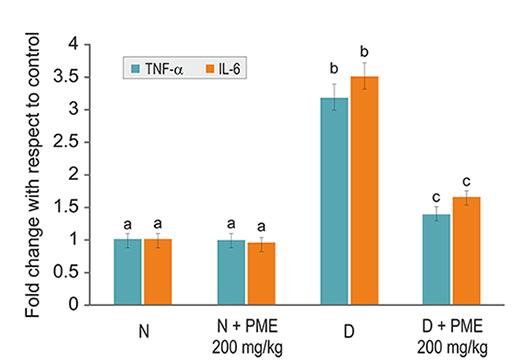
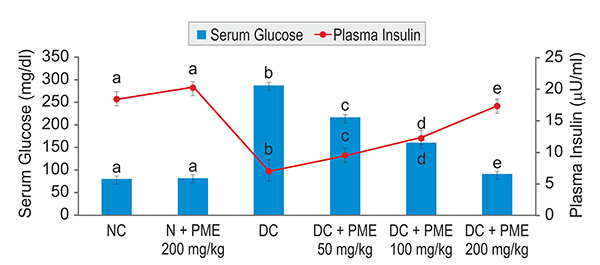
Results suggested that the highest dose of 5% fraction of PME (i.e. 200 mg/kg) produced a significant reduction in the levels of serum glucose (p<0.05) and increase the plasma insulin (p<0.05) at the end of the study (Fig.1). Similarly, at 200 mg/kg dose, 5% PME fraction demonstrated significantly (p<0.05) decreased levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL, while the level of HDL was significantly increased. Level of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) in rats treated with 5% PME (200 mg/kg) was significantly reduced (p<0.5) and was close to the normal value (Table 1). 5% PME significantly reversed the altered activities of the key enzymes of lipid metabolism to near normal levels. Group treated with 5% PME (200 mg/kg) demonstrated a significant reduction in oxidative stress and levels of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) (Fig. 2), messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), as well as protein expression and caspase-3 enzyme (apoptotic marker) in liver tissues of diabetic rats. Histopathological examination of liver and pancreas showed good correlation with data from biochemical evaluation.
In conclusion, P. marsupium may be useful in the management of diabetes owing to its anti-inflammatory, antihyperglycemic, and antihyperlipidemic potential.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| *p<0.05 vs. Diabetic group | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Table 1: Effect of P. marsupium extract 5% on the lipid profile and HbA1c levels. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||